- Joined
- Dec 11, 2018
- Messages
- 1,185
- Trophies
- 0
Citing unnamed sources familiar with the matter, DigiTimes said TSMC will continue being Nvidia's main source of chips for the upcoming GPUs, which shouldn't come as a surprise. TSMC is a long-standing Nvidia partner, and the Taiwanese foundry has sufficient production capacity to fill big orders. Nvidia has reportedly put in a significant 7nm order for its upcoming Ampere graphics cards, which could include the RTX 3080 line.
Furthermore, Nvidia has even reportedly reserved TSMC's 5nm production capacity in 2021 for Hopper, which is believed to be the microarchitecture succeeding Ampere. This would be wise on Nvidia's part, considering that TSMC is pegged to produce Apple's 5nm Arm-based processors and AMD's rumored Ryzen 5000-series CPUs.
So where does that leave Samsung? Anonymous sources have whispered to DigiTimes that Nvidia is tapping Samsung to produce lower-end Ampere graphics cards. By doing this, Nvidia could effectively lessen the load on TSMC and maximize the yields from both foundries.
It's currently speculated that low-end Ampere products could leverage Samsung's 7nm EUV or 8nm process nodes. Samsung seemingly transitioned to the newer and improved 5nm EUV manufacturing process in the second quarter of this year, DigiTimes said. Its sources also claimed that Nvidia and Samsung are in negotiations as to whether the latter can get a small piece of Nvidia's 5nm orders.
For those interested in MCM-GPU tech, Nvidia did some research on it back in 2017.
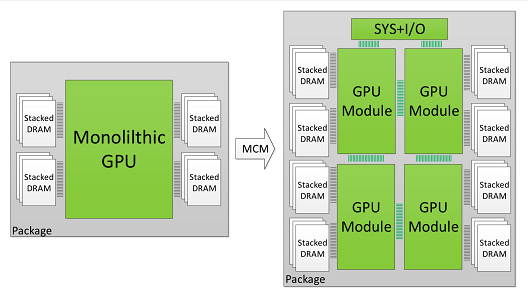
The proposed Multi-Chip Module GPU (MCM-GPU) architecture is based on aggregating multiple GPU modules (GPMs) within a single package, as opposed to today’s GPU architecture based on a single monolithic die. This enables scaling single GPU performance by increasing the number of transistors, DRAM, and I/O bandwidth per GPU. Figure 1 shows an example of an MCM-GPU architecture with four GPMs on a single package that potentially enables up to 4× the number of SMs (chip area) and 2× the memory bandwidth (edge size) compared to the largest GPU in production today.
We show that with these optimizations, a 256 SMs MCM-GPU achieves 45.5% speedup over the largest possible monolithic GPU with 128 SMs. Furthermore, it performs 26.8% better than an equally equipped discrete multi-GPU, and its performance is within 10% of that of a hypothetical monolithic GPU that cannot be built based on today’s technology roadmap.

TSMC obtains major orders for Nvidia next-gen 7nm and 5nm GPU, sources claim
Speculation is circulating that Samsung Electronics' 5nm EUV process has attracted orders from Nvidia for its next-generation graphics processor series, but sources familiar with the matter believe TSMC will remain the major foundry partner of the chip vendor for its 5nm as well as 7nm GPU families.
www.digitimes.com

Report: Nvidia Places 7nm, 5nm Orders for Next-Gen Ampere, Hopper Graphics Cards
Preparing for the not-so-distant future